Transformations suffered by sofosbuvir in the liver:
- Isopropyl ester hydrolisis. Catalised by catepsin A (CatA) or carboxylesterase 1 (CES1).
- Release of phenol group attached to phosphate, by internal nucleophilic attack of carboxylate to phosphate. A spontaneous reaction.
- Deamination, releasing alanine. Catalised by Hint1.
- Phosphorilation to diphosphate. Catalised by UMP-CMP kinase.
- Phosphorilation to triphosphate. Catalised by nucleoside diphosphate kinase.
Triphosphate is the active drug, a potent inhibitor of NS5B, the RNA polymerase in HCV virus. Being a structural analogye of UTP (the substrate) allows it to bind the catalytic centre of NS5B.
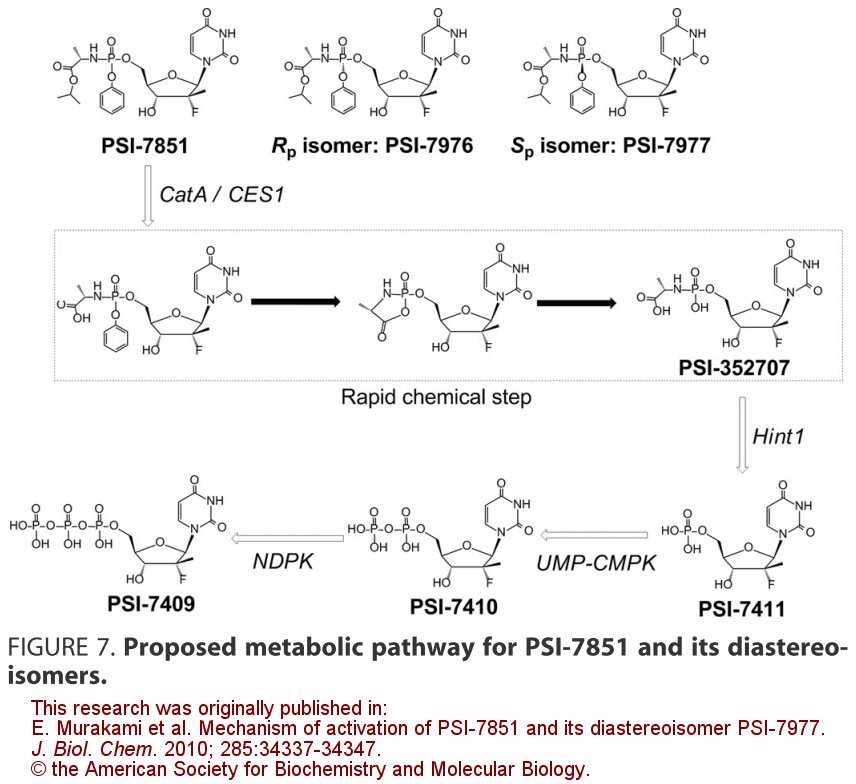
Figure reproduced according to conditions set by the publisher.
E. Murakami et al. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.161802

