 An example of triacylglycerol: 1-oleoyl-2-linolenoyl-3-linoleoylglycerol
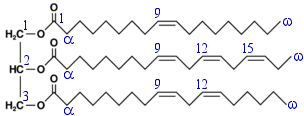
An example of triacylglycerol: 1-oleoyl-2-linolenoyl-3-linoleoylglycerol Triacylglycerols (formerly called triglycerides) are the major components of (solid) fats and (liquid) oils. Their properties vary depending on which are the 3 fatty acids that make them up.
 An example of triacylglycerol: 1-oleoyl-2-linolenoyl-3-linoleoylglycerol
An example of triacylglycerol: 1-oleoyl-2-linolenoyl-3-linoleoylglycerol
1) oleic acid, 18:1Δ9, 18:1n−9, or 18:1ω−9
2) alpha-linolenic acid, 18:3Δ9,12,15, 18:3n−3, or 18:3ω−3
3) linoleic acid, 18:2Δ9,12, 18:2n−6, or 18:2ω−6
Linoleic is an "omega minus 6" fatty acid, while linolenic is an "omega minus 3".
A triacylglycerol such as this ones, with poliunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), has a low melting pointand will be part of oils.